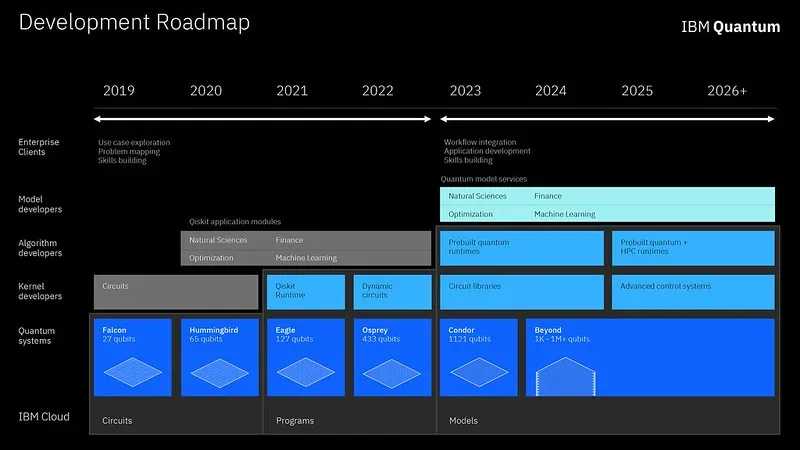
Only recently IBM published it’s Quantum Computing Roadmap. Never sleeping, big blue has made new waves with its recent announcement where [IBM] unveiled a plan to radically speed-up adoption of quantum computing by streamlining and simplifying the quantum programming tools.
IBM is the originator of one of the most popular open-source quantum computer languages: Qiskit. For the last four years IBM has opened the doors to the public to run circuits on their cloud based quantum services. Anyone with an internet connection can run quantum circuits – either simulated with Qiskit or running on IBM’s own hardware situated in one of their labs.
IBM’s aim is to make hardware disappear seamlessly into the background. Just as we do right now with our computing. Few us care about gate operations such as NANDs, bit shifts and how binary patterns are manipulated at their core. Instead we have moved further up the “stack” which enables us to piece together higher level abstractions into making code, models and products that work.
Looking to 2025 and beyond, we think that our dream of frictionless quantum computing will become a reality
IBM on quantum computing
Currently programming a traditional gate based quantum computers means programming or coding a quantum circuit. The circuit consists of a series of gates (rather analogous to classical) that operate on qubits instead of bits. Gates such as CNOT’s H’s (Hadamard) and NOT can all operate on these qubits. IBM hopes that by 2030 companies are running billions if not trillions of quantum circuits on their Hardware.

The key to getting more applications running on IBM hardware is to ensure that users can seamlessly and easy port over their applications to run in the quantum space. As you would expect IBM is delivering a series of innovations and tools besides just pure grunt (qubit count). We take a look at some of those subtler innovations.
Ideally developers should be able to use their existing tools and technologies rather then having to learn an entire new technology and framework. This would be a major win for IBM and users if the company can pull it off. It took sixty years between transistors and the cloud based systems we employ today. IBM wants to achieve the same thing, but for Quantum only much much faster.
A new Qiskit runtime means that applications can be run closer to the hardware, which could offer a 100x speed-up.
Another application is dynamic circuits, where different paths can be executed depending on an intermediate measurement result.
Mid circuit measurements and mid circuit resets are yet another innovation that IBM has successfully demonstrated. By 2023 IBM anticipate pre built run-times for both classical and quantum hardware. 2021 will see IBM run Quantum applications 100 times faster. HPC and quantum are also on the cards to be more tightly integrated.
IBM and CQC are aligned in the mission to foster the growth of quantum computing over the next decade, both in terms of the quantum capabilities but in collective investment on the overall hybrid and quantum cloud ecosystems.
Ilyas Khan, founder and CEO of Cambridge Quantum Computing