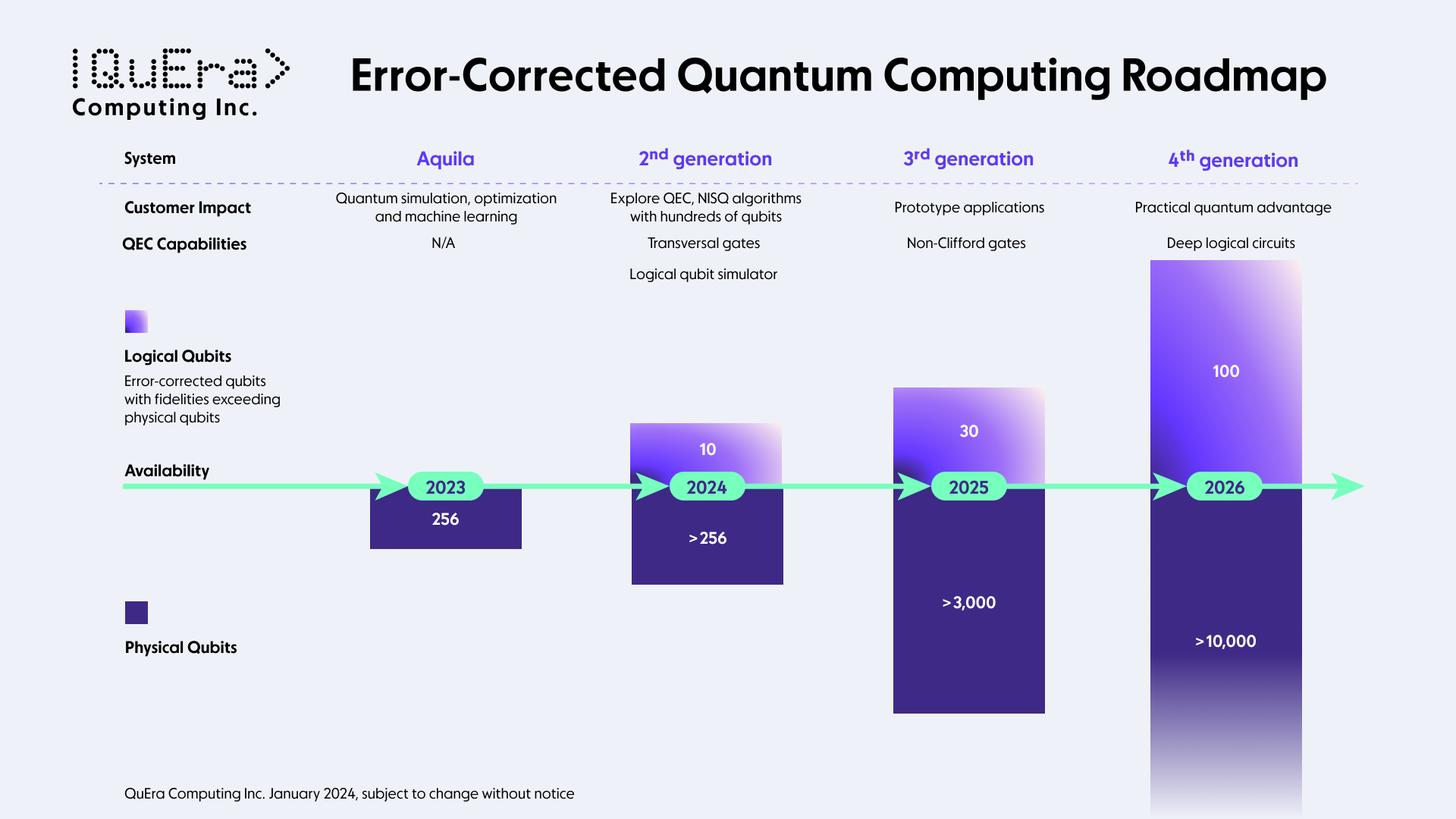
QuEra Computing has announced a strategic roadmap for a series of error-corrected quantum computers, aiming to reach 100 logical error-corrected qubits by 2026. The roadmap includes the launch of a quantum computer with ten logical qubits in 2024, an enhanced model with 30 logical error-corrected qubits in 2025, and a third-generation model with 100 logical qubits in 2026.
This development is thought will push quantum computing beyond the limits of classical simulation. The company’s CEO, Alex Keesling, and CTO, Nate Gemelke, believe this will open doors to new computational possibilities and drive innovation across various sectors and industries.
QuEra Computing Quantum Computing Roadmap
QuEra Computing, a Boston-based quantum computing company, has announced a strategic roadmap for a series of error-corrected quantum computers. The roadmap begins in 2024 and culminates in a system with 100 logical error-corrected qubits by 2026. This announcement follows a successful year for QuEra, which saw significant scientific breakthroughs, team expansion, a new investment round, and increased availability of its Aquila platform on a major cloud platform.
Quantum Error Correction (QEC) is a crucial technique that addresses the fragility of quantum states and the susceptibility of qubits to environmental interference, which can lead to errors in quantum computations. By implementing error correction protocols, quantum computers can maintain the integrity of quantum information over longer periods, enabling them to perform complex calculations that are beyond the reach of classical computers. This enhances the reliability and scalability of quantum systems and paves the way for advancements in fields ranging from materials science to drug discovery and optimization problems.
Three-Year Quantum Error-Correction Roadmap
The QuEra Computing roadmap outlines a three-phase release of its quantum computers. In 2024, the company plans to launch a quantum computer with ten logical qubits, unique transversal gate capability, and over 256 physical qubits. Transversal gates are crucial in quantum computing for their ability to prevent error propagation across qubits, making them inherently error-resistant. They simplify quantum error correction by allowing errors to be corrected independently for each qubit.
In 2025, QuEra plans to release an enhanced model with 30 logical error-corrected qubits with magic state distillation, supported by over 3,000 physical qubits. Magic state distillation enables the implementation of a broader range of quantum gates with higher fidelity, allowing for the execution of non-Clifford gates, which are crucial for universal quantum computations.
By 2026, QuEra Computing aims to introduce a third-generation quantum error-corrected model with 100 logical qubits and over 10,000 physical qubits. This development, capable of deep logical circuits, will push quantum computing beyond the limits of classical simulation, ushering in a new era of discovery and innovation.
QuEra’s Significant Achievements in 2023
QuEra Computing had a breakthrough year in 2023, marked by significant progress on multiple fronts. The company completed a $30M Series A funding round early in the year and expanded the public availability of its flagship 256-qubit Aquila system on a major cloud platform. The team has grown to include over 50 highly-skilled scientists and engineers, and the company has also bolstered its management team with experienced executives.
Scientists from Harvard, QuEra, MIT, UMD, and NIST released a series of breakthrough scientific results, providing critical building blocks for QuEra to commercially exploit as a quantum computing company.

QuEra’s Invitation to Developers, Enterprises, and HPC Centers
QuEra Computing is inviting developers to adapt their software to these groundbreaking capabilities and encouraging enterprises to explore error-corrected algorithms with logical qubits through collaboration. The company is also urging HPC centers and national programs to consider purchasing and deploying these advanced computers on-premises. For those interested in early access to these capabilities, a new waitlist page is now available.
About QuEra
QuEra Computing is a company specializing in commercializing quantum computers using neutral atoms, a highly promising quantum modality. Based in Boston and built on pioneering research from nearby Harvard University and MIT, QuEra operates the world’s largest publicly accessible quantum computer, available over a major public cloud and for on-premises delivery. QuEra is developing large-scale, fault-tolerant quantum computers to tackle classically intractable problems. For more information, visit quera.com and follow QuEra on Twitter or LinkedIn.
“With this product release plan, we are opening doors to a new world of computational possibilities,” said Alex Keesling, CEO of QuEra Computing Inc. “We are excited to leverage all the building blocks developed in past years – qubit shuttling, transversal gates, high-fidelity 2-qubit gates, and a zoned architecture – to deliver a world-leading system. It will allow us to collaborate with global partners to explore the vast potential of quantum computing and drive innovation across various sectors.”
“In a few years, the number of physical qubits will be less important to customers, and the focus will switch to logical error-corrected qubits,” said Nate Gemelke, Co-founder and CTO of QuEra. “Today, we are taking a major step in this critical transition from quantum experimentation to true quantum computing value.”
Quick Summary
By 2026, a new era of quantum computing is expected to be ushered in with the introduction of a system with 100 logical error-corrected qubits, which will push quantum computing beyond the limits of classical simulation. This advancement is part of a three-phase release of quantum computers, which will enhance the reliability and scalability of quantum systems, paving the way for groundbreaking advancements in fields ranging from materials science to drug discovery and optimisation problems.
- QuEra Computing, a quantum computing company, has announced a strategic roadmap for a series of error-corrected quantum computers, starting in 2024 and culminating in a system with 100 logical error-corrected qubits by 2026.
- Quantum error correction is a technique that addresses the fragility of quantum states and the susceptibility of qubits to interference, which can lead to errors in quantum computations. This technique enhances the reliability and scalability of quantum systems.
- QuEra’s roadmap includes a three-phase release of its quantum computers: a 10 logical qubit computer in 2024, a 30 logical qubit model in 2025, and a 100 logical qubit model in 2026.
- These advancements build upon a recent breakthrough published in Nature by a Harvard-led group, together with QuEra, MIT, NIST, and the University of Maryland, where they reported the execution of complex algorithms with 48 logical qubits.
- QuEra’s CEO, Alex Keesling, and Co-founder and CTO, Nate Gemelke, expressed excitement about the potential of quantum computing and the transition from quantum experimentation to true quantum computing value.
- QuEra invites developers, enterprises, and HPC centers to adapt their software to these groundbreaking capabilities and explore error-corrected algorithms with logical qubits through collaboration.