Citi Innovation Labs and Classiq have partnered to advance quantum solutions for portfolio optimization using Amazon Braket. The project aims to use quantum computers to study portfolio optimization, a process of selecting the optimal mix of assets to achieve the highest possible returns for a given level of risk. The study focused on employing the Quantum Approximate Optimization Algorithm (QAOA) for portfolio optimization. The results could potentially improve portfolio optimization and Citi’s complex financial challenges. The project was supported by Amazon Web Services quantum computing service, Amazon Braket.
Quantum Computing and Portfolio Optimization
Quantum computing is a rapidly evolving field with potential applications in various sectors, including finance. This article discusses a Citi Innovation Labs and Classiq project, which used Amazon Braket to explore quantum solutions for portfolio optimization.
Quantum Computing and Portfolio Optimization: The Basics
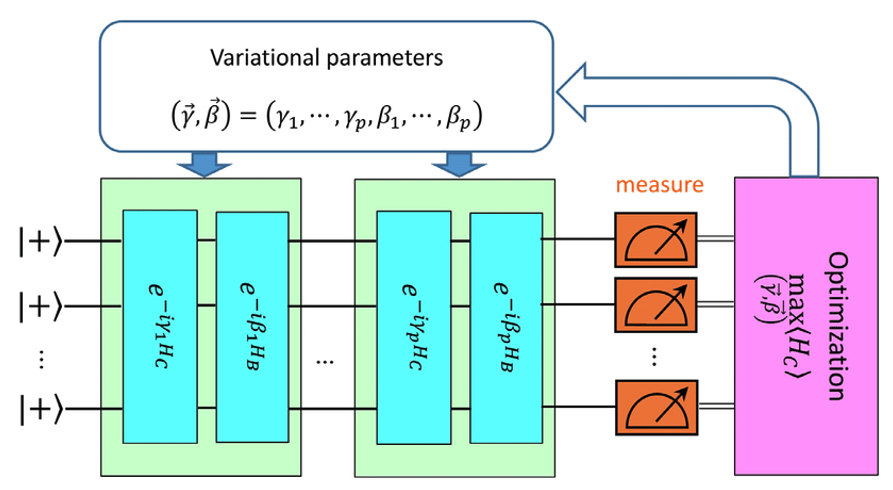
Portfolio optimization is selecting the best mix of assets to maximize returns for a given level of risk. However, the current stage of quantum computing technology, known as the Noisy Intermediate-Scale Quantum (NISQ) era, faces limitations due to noise and qubit count. This restricts the capacity of quantum applications. Despite these limitations, variational quantum algorithms, particularly the Quantum Approximate Optimization Algorithm (QAOA), are promising candidates for finding speedups over classical methods.
The project focused on using the QAOA quantum algorithm for portfolio optimization. The team investigated how adjustments to the algorithm’s penalty factor (when introducing constraints to the problem) impacted the algorithm’s performance. If the QAOA algorithm proves to have an advantage over classical methods, the strategies discussed in this project could lead to improved results in portfolio optimization and potentially other complex financial challenges.
Quantum Computation for Optimization Problems
Quantum computers exploit properties of quantum mechanics, such as superposition, entanglement, and interference, which are not accessible to classical computers. These capabilities give rise to quantum algorithms that can solve certain problems much faster than known classical algorithms. A notable example is Shor’s algorithm, which solves the integer factorization problem in polynomial time on a quantum computer, where the fastest known classical algorithm takes exponential time.
Developing new algorithms that use quantum computers to solve hard problems of relevance to industry, like portfolio optimization, is an active topic of research. Among these algorithms are quantum linear equation solvers like Harrow-Hassidim-Lloyd (HHL), which can also be used for portfolio optimization, and variational quantum algorithms like QAOA.
Modeling Portfolio Optimization with Classiq on Amazon Braket
The Classiq Software Development Kit (SDK) simplifies the process of designing and applying quantum algorithms to solve complex problems. The team used the SDK to model quantum algorithms without having to navigate the low-level details like qubit assignment and quantum logic operations.
The team collected historical stock price data for several assets, including Apple, Walmart, Tesla, GE, Amazon, and Deutsche Bank using the Yahoo Finance API (yfinance). Using this data, they calculated the expected returns and the covariance matrix, setting the stage for optimized portfolio construction.
Analyzing the Results
The team analyzed the impact on the probability of finding valid solutions when making small changes to the penalty factor while executing both the inequality and equality constraints’ QAOA circuits. They found that the quality of the results is sensitive to the magnitude of the penalty factor, which has a great impact on the quality of the algorithm. For both types of constraints, the probability to find the best 1% of valid solutions peaks when the penalty is relatively small, while increasing the penalty beyond a certain value reduces the probability of getting a good solution.
Conclusion
Citi Innovation Labs and Classiq demonstrated how quantum computing could be used to study complex problems like portfolio optimization. They used Classiq running on Amazon Braket, taking advantage of Classiq’s ease-of-use, combined with the on-demand, pay-as-you-go access to quantum hardware provided by Braket. This project highlights the potential of quantum computing in finance and the importance of ongoing research and experimentation in this field.